
Choosing which one to use will depend on the type of fluid and your purpose of measuring.

Various types of techniques and instruments can be used to measure either the dynamic (absolute) or the kinematic viscosity of a fluid. For example, the IUPAC standard conditions for liquids and gases are defined as: 273.15 K (0 ☌) and 100 kPa (roughly 1 atm). The conventional or standard temperature and pressure, however, may actually vary they’ll depend on what you want to measure and the international convention that you want to use. Therefore, viscosity is technically a measure of the speed of the flow of fluids under a given set of standard conditions.Įxternal factors, such as pressure and temperature, must be maintained at a constant to have an accurate and standardised measurement of viscosity. Since the resistance force of the fluid cannot easily be measured in a direct manner, flow rate can be used as a surrogate. Viscosity is the resistance of fluids to flow or deform at a given rate. The unit of measure for kinematic viscosity is square metre per second (m 2/s) The measurement is dependent on the density of a fluid. It’s basically how a fluid resists the pull of gravity. Kinematic viscosity : This is measured against the force of gravity.The unit of measure for absolute viscosity is millipascal seconds (mPa-s). It’s the ratio between the shear stress applied and the area of the sample fluid. Dynamic viscosity : This is otherwise known as the absolute viscosity, and is related to the force under which a fluid is subjected.There are two types of viscosity you can measure: dynamic and kinematic: Therefore, viscosity can be considered as internal friction between particles of a fluid. Similarly, the actual viscosity of fluids is dependent on how the particles (molecules) of the fluids move against each other. But if you were to use bigger sand particles, the sand would either move slower or become stuck. Conversely, the solid analogues of liquid and gaseous fluids also exhibit a solid-like structure when the individual particles are too crowded in a container.įor example, very fine particles of sand can easily flow through the narrow opening inside an hourglass.
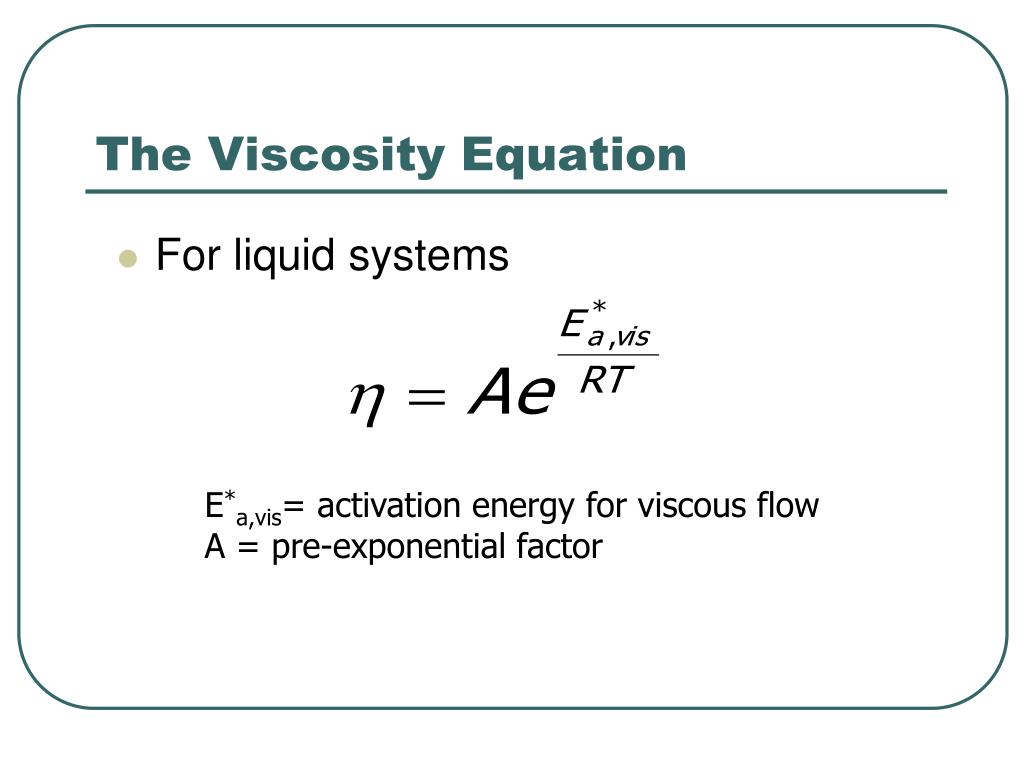
In some instances, solids can also exhibit fluid-like properties, such as the ‘flow’ of wheat grains moving inside in a pneumatic conveying system. Molecules of the same type have cohesive force among the particles, which is difficult to break.įluids are substances that flow, and they can either be liquids or gases. The resistance is also correlated with the intermolecular forces. If the particles are closer together, the fluid tends to be more viscous. This resistance is because of the way the particles are arranged. Viscosity is the resistance of particles in a fluid to flow or move in response to an external force exerted on them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
